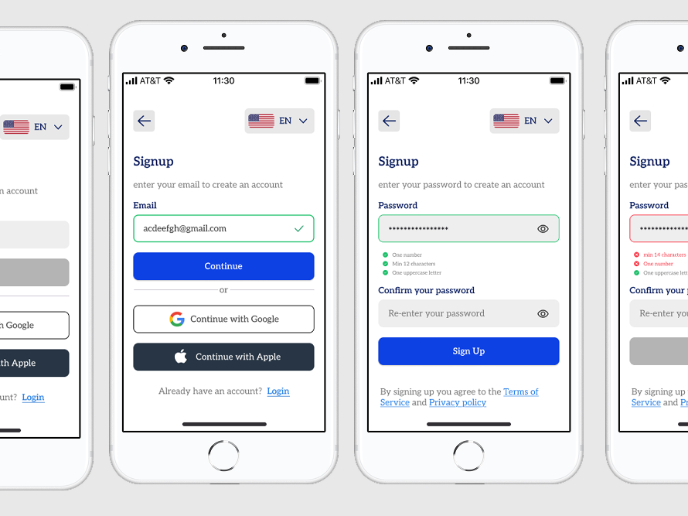
Login
Login is the process where users authenticate their identity by entering credentials, granting them access to a digital system, service, or account.

TL;DR
- Grants users access to accounts or systems.
- Commonly requires username and password.
- Increasingly includes multi-factor authentication.
- Critical for security, privacy, and trust.
Definition of Login
Login is the process of verifying a user’s identity, typically through credentials like usernames, email addresses, and passwords, to grant secure access to a product or service.
Detailed Overview
Login is one of the most common interactions in digital systems. It provides the gateway between public-facing experiences and private, personalized ones. At its core, login verifies that a user is who they claim to be, protecting both the individual’s data and the integrity of the system.
A frequent question is why login remains so important when alternatives like guest access exist. The answer lies in personalization and security. Login enables personalized experiences, such as saved settings, purchase history, or progress tracking, while also ensuring sensitive data is shielded from unauthorized users. Without login, systems cannot reliably protect or customize content.
Another common discussion involves credentials. Traditionally, login relied on a username and password. However, passwords pose risks, including reuse and weak choices. Many products now support passwordless authentication through methods like magic links, biometric scans, or social sign-ins. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of security, requiring verification beyond a single password.
Login friction can drive users away, especially if the process is lengthy or error-prone. Features like “remember me,” password managers, and single sign-on (SSO) reduce barriers. Balancing usability with security is a recurring challenge for product teams. For instance, a banking app may require stricter controls than a news site, because risk profiles differ.
Accessibility also comes up frequently. Login processes must be compatible with assistive technologies like screen readers and must support keyboard navigation. CAPTCHA challenges, often used for bot prevention, can create barriers if not implemented with alternatives such as audio prompts.
Finally, login design directly influences trust. Clear error messages, consistent handling of failed attempts, and transparent communication about why authentication is required help reassure users. Products that make login feel smooth and reliable increase user confidence, while confusing or broken login flows drive abandonment.
Learn more creating great login experience with the Login & Signup Flows Lesson, a part of the Common Design Patterns Course.
Login protects personal data and allows for personalized experiences. Without it, systems cannot verify identity or provide features like saved progress, purchase history, or account-level preferences.
Beyond personalization, login ensures that only authorized users access sensitive or private information, which is critical for both security and compliance.
Passwords are often weak or reused across services, making them vulnerable to breaches. Users also forget them frequently, creating frustration and recovery challenges.
For this reason, many systems now adopt passwordless methods or strengthen authentication with multi-factor checks, balancing convenience and safety.
Reducing friction is key. Features like “remember me” options, integration with password managers, and single sign-on simplify the process. Short, clear error messages help users recover quickly from mistakes.
The design should balance ease of use with security. Too much friction leads to abandonment, while too little weakens protection.
Login must work for everyone, including those using screen readers, keyboards, or other assistive technologies. Poorly designed CAPTCHA or unclear labels can exclude users. Alternatives, such as audio CAPTCHAs and proper form labeling, are necessary to ensure inclusivity.
Accessible login experiences create trust and broaden adoption across diverse user groups.
Trust depends on both security and clarity. A system that communicates why credentials are needed, handles errors gracefully, and provides transparent recovery options reassures users.
Conversely, unclear or broken login flows erode trust, leading to abandonment and negative impressions of the product.
Recommended resources
Courses

UX Design Foundations

Design Terminology

Common Design Patterns
Lessons
Exercises
Projects

Reset Password - Mobile App Flow

Siter.io Signup & Login A11Y